Description
STRUCTURE
Sequence: H-Glu(H-Lys-OH)-OH
Molecular Formula: C11H21N3O5
Molecular Weight: 275.30 g/mol
CAS Number: 17105-15-6
Peptide purity: greater than 98%
Other details: No TFA Salt, No Mannitol
Storage: Lyophilized peptide must be stored at -20°C and peptide solution at 4°C.
Retilanamin has low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability.
DESCRITPION
In the structure of the eye retina (nervous tunic of the eyeball) is one of the thinnest layers, being the most complex and highly differentiated tissue. Its complex structure makes it sensitive to light, allowing to perceive colour and images and to convert them into a signal being sent straight to the brain. Position of the retina behind other optic structures, direct ingress of sun rays, peculiarities of the blood supply make it vulnerable to both external (sun rays, light striking, radiation) and internal factors. Retina is as a rule damaged in case of the following diseases: hypertension, diabetes mellitus, renal insufficiency etc. Smoking and alcohol consumption also negatively affect retina. It should be noted that any damage of the retina can lead to the impaired vision or even to complete blindness.
Among the most frequent retinal diseases there are age-related macular degeneration, hereditary retinal degenerations (including retinitis pigmentosa), complicated myopia, diabetic retinopathy. Modern methods of treatment based on the application of the known pharmaceutical substances do not lead to significant results. Usually a prognosis for a disease of these patients is unfavourable (gradual and progressive decrease in the visual functions up to blindness).
First reliable positive results of retinal diseases treatment were achieved in the middle 1980ies in Leningrad (Saint Petersburg). The results of the studies conducted at the research laboratory of the S.M. Kirov Military Medical Academy headed by V.Kh. Khavinson served as a basis for the modern concept of peptide regulation of human organism.
In case of introduction into the organism, peptides become inductors of synthesis of the specific proteins, capable of restoring tissues, damaged by a disease or with ageing.
One of the first preparations designed at the Institute was a peptide complex isolated from the cattle retina – Retinalamin. Experimental and clinical studies revealed its high efficiency in the treatment and restoration of retinal functions if compared to the known methods. In the clinical practice this preparation turned out to be highly effective in the treatment of the aftereffects of retinal veins thrombosis, glaucoma, haemorrhagic retinopathies, retinal sun and laser burns and many other diseases.
At the same time there were also conducted clinical trials of other peptides, isolated from the pineal gland, thymus, cortex, vessels and other organs (Epitalon, Cortagen, Thymalin, Slavinorm).
The efficiency of the complex application of these peptide preparations in case of different retinal pathology was considerably higher if compared to the separate application.
Recently at the Saint Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology, a unique method for restoration of the damaged retina based on the application of peptide bioregulators was developed. A set of peptides for the treatment course is designed taking into consideration specificity of the eye ball structure, and depending on the allocation and type of the damage as well as on the general state of the patient it includes peptides of the retina, thymus, pineal gland, cortex, vessels and other. It turned out that peptide bioregulators are most effective in case of age-related macular degeneration, retinitis pigmentosa, complicated myopia, diabetic retinopathy.
In recent years the Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology has synthesized and studied a new group of peptide bioregulators being analogues of the complex peptide preparations. The activity of these preparations is higher than that of the earlier designed. These are short peptides (2-4 amino acids) of the retina, pineal gland, cortex, thymus, vessels etc.
These peptides (Normoftal, Pancragen, Vesugen, Crystagen, Pinealon and others) are widely used in the medical practice as the means for prevention and treatment of different eye diseases.
Diabetic retinopathy
One of the most severe complications of the diabetes mellitus is a diabetic retinopathy, that is a progressive lesion of the retina, requiring laser and surgical intervention.
Peptide bioregulators enhance activity of the blood antioxidative system, including enzymes of the antioxidative defence, due to neutralization of highly toxic hydroxyl and peroxyl radicals, generated in the process of free radicals oxidation, this being very important in case of diabetes. They contribute to restoration of the damaged structures of the vascular wall and intercellular contacts restoration, affecting processes of the intracellular regulation. As a consequence they resolve haemorrhages and plasmorrhages, lessen edemata, regenerate and enhance cellular living potential.
Retinitis pigmentosa
Retinitis pigmentosa is one of the most severe and frequent hereditary retinal diseases.
Diagnosis: Pigment retinal degeneration in both eyes, low myopia in both eyes, pseudophakia in the left eye, initial cataract in the right eye. The patient was being observed at the Medical Centre of the Saint Petersburg Institute of Bioregultaion and Gerontology from 2003 till 2010. He underwent 12 courses (10 days each) with a complex of bioregulators. During the period of observation there were being registered significant widening of the field of vision and considerably improved ERG indices. After the first treatment they reported increased visual acuity, significant widening of the fields of vision, improved scotopic (twilight) vision.
Field of vision test (computer based perimetry, 'Pericom')
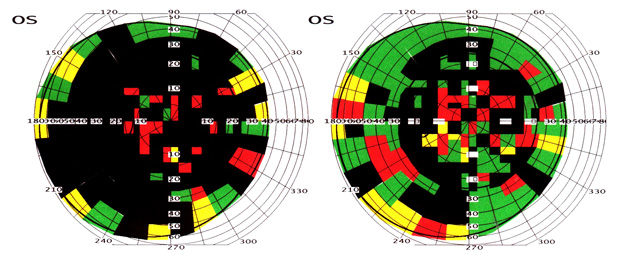
Results: There was positive clinical result after complex treatment including Retinalamin in all cases (improvement of visual acuity, peripheral field condition). Effect of Retinalamin treatment became apparent at the end of 1 month after treatment and even more evident after second course. Clinical effect was stable during half a year.
Age-related macular degeneration
Peptide bioregulators are effective in the treatment of both wet and dry macular degenerations.
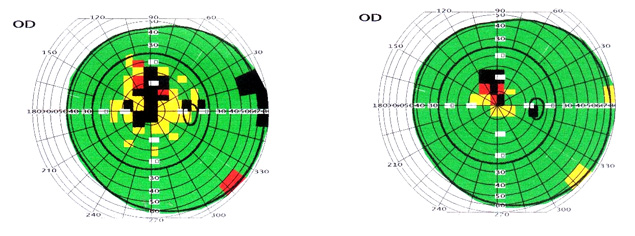
Diagnosis: age-related macular degeneration, initial cataract, hypertonic retinal angiopathy in both eyes.
The patient has underwent 2 courses (10 days each) with a complex of bioregulators. During the period of observation there were being registered significant widening of the field of vision and considerably improved ERG indices.
Field of vision test (computer based perimetry, 'Pericom')
Other eye diseases
Encouraging results were obtained in case of treatment of other diseases associated with retina functions impairment. For instance, high myopia is often associated with the complications such as haemorrhages and (or) retinal degenerations. This causes a significant impairment of visual functions and even complete blindness. Administration of Retilanamin and other peptide bioregulators allows to reduce severity of these complications and achieve significant positive dynamic in visual functions.
Fast and pronounced improvement is also registered when peptide bioregulators are administered in patients with macular retinopathies of different etiology (chorioretinitis, burns (sun burns, laser burns), central serous chorioretinopathy etc.
Retinalamin was shown to have a positive effect on the acuity and the quality of vision of myopic patients. A statistically significant positive change of the major parameters of light sensitivity of the visual field was noted. The data of electrophysiological studies revealed a positive effect of retinalamin on the functional activity of the retina, especially in its central sections. The achieved effect was stable over the whole follow-up period (up to 3 months after the course of treatment).
Primary open-angle glaucoma
Results: after Retinalamin administration clinically significant results were noted in 3, 6, 12 months (extending of the visual field boundaries, increasement of visual acuity, stabilization of the process according to ophthalmoscopy, increasement of the average thickness of retinal nerve fibers). At the end of the follow-up period in majority of patients of the control group we observed progression of POAG.
REFERENCES
J. Ambati et al., "Age-related eye disease study caveats" [PubMed]
M.J. Barondes et al., "Controlled trial of laser photocoagulation of pigment epithelial detachments in the elderly: 4 year review" [PubMed]
N.V. Makashova et al., "Application of Retinalamin for the treatment of glaucomatous optic neuropathy" [PubMed]
A.A. Suetov et al., "Retinoprotective effects of Retinalamin studied in an experimental model of photochemical damage to rabbit retinas" [PubMed]
E.I. Aleksandrov et al., "Treatment with the peptide bioregulator retinalamine in patients with tuberculosis of the organ of vision" [PubMed]
A.F. Gabdrakhmanova et al., "Molecular mechanisms of neuroretinoprotection in primary open-angle glaucoma" [PubMed]
T.E. Aleksandrova et al., "Results of retinalamine use in the treatment of tuberculous chorioretinitis" [PubMed]
A.V. Khvatova et al., "Polypeptide bioregulators in the treatment of different-type abiotrophy of the retina" [PubMed]
E.A. Egorov et al., "Structural and functional changes in the retina of patients with primary open-angle glaucoma and compensated intraocular pressure while undergoing retinoprotective therapy" [PubMed]
V.P. Erichev et al., "Peptide bioregulators: delivery and efficacy" [PubMed]
S.E. Avetisov et al., "Evaluation of therapeutic sensitivity of retinal ganglion cells to targeted peptide bioregulator in culture" [PubMed]
S.B. Trofimova et al., "The effect of the bioregulating therapy on the quality of life of elderly patients with retinal pathology" [PubMed]
V.Kh. Khavinson et al., "Effects of peptides on proliferative activity of retinal and pigmented epithelial cells" [PubMed]
V.V. Strakhov et al., "The influence of long-term retinal protective therapy on glaucoma progression according to structural and functional tests" [PubMed]
V.Kh. Khavinson et al., "Inductive activity of retinal peptides" [PubMed]
D.A. Dorofeev et al., "Effect of retinal protective therapy on optical coherence tomography angiography (pilot study)" [PubMed]
S.V. Trofimova et al., "Effectiveness of bio-regulators in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy" [PubMed]
S.V. Kharinsteva "Retinoprotective therapy of diabetes macular edema in elderly patients" [PubMed]
V.V. Strakhov et al., "Structural and functional changes in the retinal layers in patients with primary glaucoma and possible means of retinoprotection" [PubMed]
DISCLAIMER
This product is intendend for lab research and development use only. These studies are performed outside of the body. This product is not medicines or drugs and has not been approved by the FDA or EMA to prevent, treat or cure any medical condition, ailment or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law. This product should only be handled by licensed, qualified professionals.
All product information provided on this website is for informational and educational purposes only.